
Graduate Management Aptitude Test is an International Computer Adaptive Test conducted at over 600 test centers across 114 countries. The examination evaluates the Analytical, Quantitative, Verbal and Reading, and Written Communication. GMAT is taken by students aspiring to pursue management education viz. Masters in Business Administration (MBA), Masters in Management (MIM), and Executive MBA at top-notch B- schools across the world. The GMAT examination is conducted by GMAC. GMAC not only administers the GMAT examination, but it also plays a part in providing study materials (Official Guides), Practice Tests, and in making available the scores to universities across the globe and verifying the student scorecards.
The GMAT examination was first started in the year 1953 and was taken by just more than 2000 test-takers in the initial years, but today it is the most popular management entrance examination across the world with more than 200,000 candidates writing the exam annually. The GMAT exam consists of four sections: Analytical Writing Assessment, Integrated Reasoning, Quantitative Aptitude, and Verbal Aptitude. The examination lasts for more than three hours and one of the most important aspects of the GMAT examination is also time management.
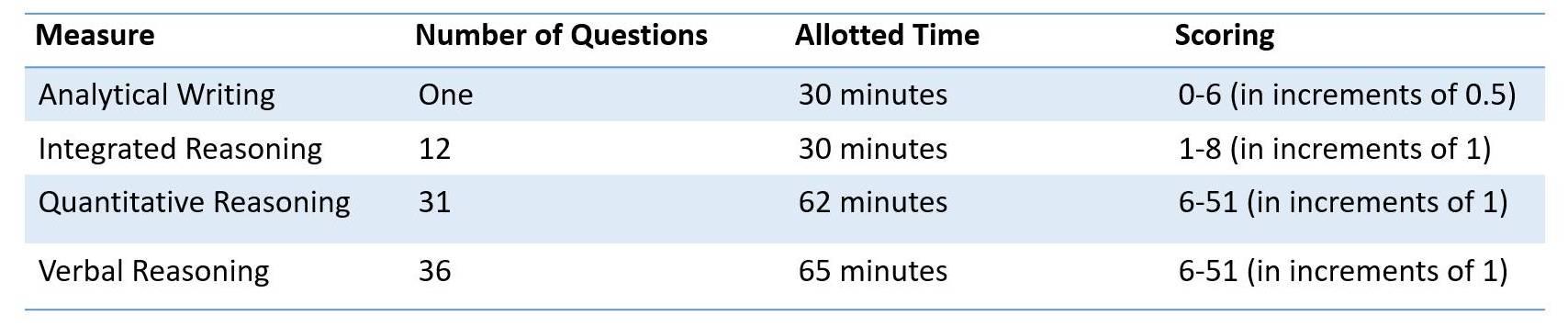
***The total duration of the exam is three hours and seven minutes.
Before registering as a candidate for the GMAT exam one must know the eligibility criteria. Following are the key points required to assess your eligibility for this examination:
The steps to register for GMAT is as follows

After the payment of the GMAT examination fees, candidates will receive a confirmation mail acknowledging the payment and with the details of the schedule chosen by the student. Apart from scheduling their exams online, a candidate can also schedule their exam by contacting GMAT Customer care service by phone. The GMAT exam is conducted in a total of 17 different centers in India – Delhi, Bangalore, Kochi, Indore, Pune, Mumbai, Hyderabad, Visakhapatnam, Ahmedabad, Ranchi, Nagpur, Chennai, Jaipur, Coimbatore, Lucknow, Kolkata, and Chandigarh.
Integrated Reasoning: This section tests the ability to evaluate and assess the data presented in the form of a graph or table. This section consists of 12 different kinds of questions of the following type

Quantitative Reasoning: The quantitative section comprises two sections including Data Sufficiency and Problem Solving. The questions are objective types and will have multiple choices as answers. There will be 18 questions from Data sufficiency and other 18 questions from the Problem-Solving part. In Problem-solving questions, a candidate’s logical reasoning is assessed as they have to use analytical reasoning to solve these quant questions, whereas, in Data sufficiency a candidates ability to examine a problem is assessed as they have to identify which data is important and at what point there is enough data to solve the given problem.
The Quantitative Reasoning topics are further divided into the following categories: Geometry, Elementary Algebra, Ratio and Proportions, Properties of Integers, Permutation and Combination, Exponents and Roots, Arithmetic, Linear Equations, Multiples and Factors, Inequalities and Basic Statistics, Mixtures and Alligations, Descriptive Statistics, Speed Time and Distance, Simple and Compound Interest.
Verbal Reasoning: This section consists of 36 multiple-choice questions. This section is divided into Critical Reasoning, Reading Comprehension, and Sentence Correction. This section also analyzes a candidate’s ability towards writing skills and reading skills and they have to assess the logical relationship between the points mentioned in the passage and the concepts.
The following areas will be covered in the verbal reasoning section: Critical Reasoning, Rhetorical Construction of Sentences, Sentence Correction, Reading Comprehension, Subject-Verb Agreement, Misplaced Modifiers, Countable vs Uncountable Nouns, Parallelism, Verb Tenses
Analytical Writing Assessment: This section will be consisting of a topic on which the candidate has to write an essay (Opinion based on a query that is posed). A passage may be given from which the questions may be asked and based on the given passage the candidate has to answer the questions, this will analyze the candidates’ skill to draw in inferences and how well he understands the text. The way to attempt this task is not to assess the argument but to come out with your opinion on the argument. This task is not the test of your opinion but a test of your writing style.
The overall GMAT score ranges from 200 to 800. Candidates are scored based on a fixed scale on all the sections of the GMAT exam. The GMAT scorecard consists of GMAT Verbal score and GMAT Quant score. On average the test-takers score between 400 to 600. Most of the prestigious B – schools like The Harvard Business school, Wharton School, Stanford Graduate School of Management, The University of Toronto, Kellogg School of Management, etc. all of these accept a minimum score of 650 and above, but these top B-Schools will look for a score of above 720+ if your profile is not extraordinary.
Who should be taking this exam? Does it ever expire?
GMAC charges you a sum of US $250 for the registration of the GMAT exam. One can also reschedule their exam but to reschedule your exam one has to pay a sum of US $50 every time they reschedule their exam. But in case a candidate wants to cancel their exam a sum of US $80 is charged. One can pay their GMAT exam registration fees either by online or offline modes.
Following are the tips and strategies a candidate must follow during the prep time of their GMAT exam: